The Call Recording Model
This section describes how call recording works. It also provides an overview of the recording model.
Call Recording proceeds in three stages:
- Initiating
- Progressing
- Ending
as described in the following sections.
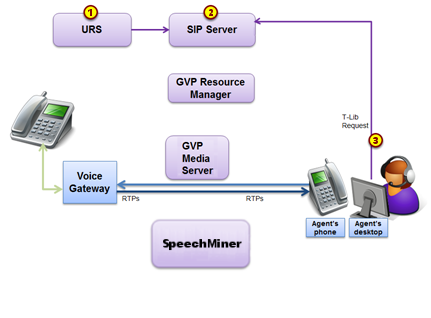
Call Recording Initiated
There are three ways that recording can be initiated. Once started, the recording process is the same, regardless of how it was initiated.
One of the following initiates recording:
- A recording can be initiated by a Routing Strategy (1).
- SIP Server initiates full time recording based on DN configuration (2).
- Agent Desktop requests call recording through Interaction Workspace (3).
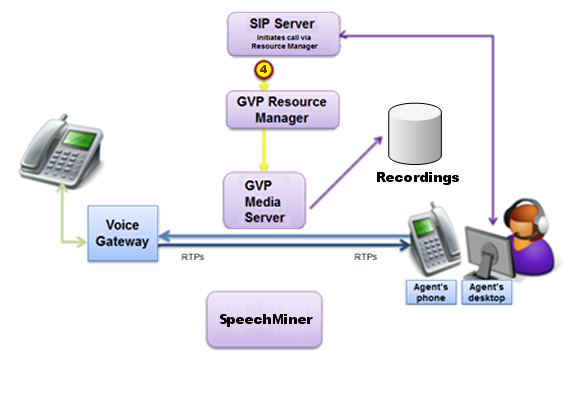
Recording in Progress
Using media control, SIP Server invites Media Server to bridge the media path between parties and at the same time record the call to a file (4).
Recording Ends
When the recording ends, SIP Server re-invites the session to have media sent directly between the parties. Media Server submits the recording to storage and to the Recording Processor (5).
Recording Processor then consolidates call events about the recording (for example, across switches) and submits the information to SpeechMiner and Interaction Recording Web Services (or Web Services if you're using version 8.5.210.02 or earlier) (6).
After indexing has been completed by SpeechMiner, the recording is made available through the SpeechMiner interface (7).
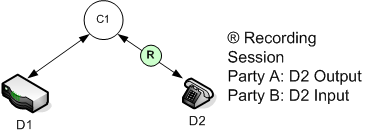
Call Recording Model
The basic model for initiating call recording is based on the SIP Server connection model. Recording is initiated from the termination device; it is known as agent-side recording: