Dialed_Number_Identification_Service
Also known as DNIS. A feature of 800 or 900 lines that identifies the telephone number that the caller dialed to reach the attached computer-telephony system.
Glossary
Automatic_Number_Identification
Also known as ANI. A feature that passes a caller’s telephone number over the network to the receiving location, so that the caller can be identified. Sometimes referred to as a “Caller ID.” ANI is a North American term, and Calling Line Identification (CLI) is an alternative term that is used elsewhere.
Glossary
Universal Routing Server
Also known as URS. The server that is used by Universal Routing that automatically executes routing-strategy instructions and distributes incoming customer interactions among contact-center agents. Previously known as Interaction Router.
Glossary
Routing_Point
Also known as an RP. Any point at which interactions wait for routing by Universal Routing Server (URS). These points have different names on different Private Branch Exchange (PBX) switches (for example, CCT, CDN, and VDN). Switches often have a script that is associated with them and that directs calls to a destination.
Glossary
Universal_Routing
A Genesys CIM Platform component that provides voice-routing capabilities When it is combined with Multimedia, various types of non-voice media can also be routed. These two components work together to enable seamless routing of both voice and non-voice interactions. More information on Universal Routing is provided here.
Glossary
Universal Routing Call Flows
This page illustrates voice inbound call flows that use Genesys Universal Routing.
Voice interactions that arrive at the switch are delivered to a Routing Point. Universal Routing Server (URS) uses ANI, DNIS, or the date and time of day to collect information and select an appropriate routing target. Basic targets are ACD queues and individual DNs. More advanced targets are agent groups, place groups, and skill expressions.
The following call flows are supported:
- Inbound interaction — Routing Point routes to ACD queue
- Inbound interaction — Routing Point routes to agent
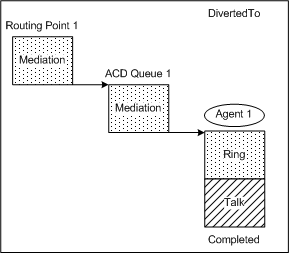
Inbound interaction — Routing Point routes to ACD queue
| This call topology shows the outcome of a call that is routed to an agent via an ACD queue. The call arrives at the Routing Point. The Routing Point then routes the call to an ACD queue, and the interaction is diverted to an agent.This applies to both network routing and enterprise routing. For network routing, Routing Point 1 could be a service number on a network T-Server that routes the voice interaction to ACD Queue 1 on a premise T-Server.
Technical Descriptors illustrated:
|
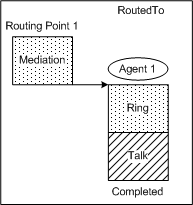
Inbound interaction — Routing Point routes to agent
| This call topology shows the outcome of a call that is routed directly to an agent. The call arrives at the Routing Point. The Routing Point then routes the call to an agent.This applies to both network routing and enterprise routing. For network routing, Routing Point 1 could be a service number on a network T-Server that routes the voice interaction to Agent 1 on a premise T-Server.
Technical Descriptors illustrated:
|