Contents
TURN Server Installation and Configuration
Existing TURN Server (Non-Genesys)
If you already have a TURN server deployed in your network and prefer to use it instead of the Genesys Video TURN Server, then do the following:
- In the web-client configuration, use the existing TURN server(s) address and port.
- For Application Server setting for the TURN server, check TURN Configuration in Application Server Settings.
- In the TURN server settings, add a user mcu with password as set in the previous step (default -- fGui712nJw).
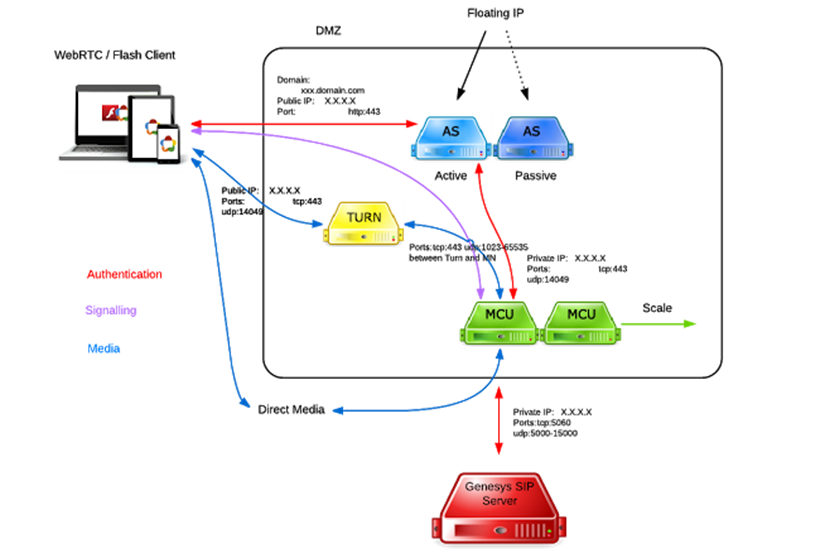
Genesys Video TURN Server
Host Requirement
- CentOS 6.x.
- At least two vCPUs, 4GB Memory. SSD is preferred, but not mandatory.
- The most important factor is the networking performance.
Port Requirement
TURN server port requirements are described in the Port Usage section.
The Collaboration TURN Server IP for TURN server is available with this release and must be installed on a separate server.
You must have sudo access to install the TURN server. To configure the server:
- Set multilib_policy=all to the /etc/yum.conf file.
- Install the following libs:
sudo yum install perl-libwww-perl ntp openssh-server wget bzip2-devel bzip2-libs libXtst zlib-devel libcrypto.so.6
- Ensure Selinux is disabled by editing the /etc/sysconfig/selinux file, and make sure that this line is set to disabled:
SELINUX=disabled
- Turn off the firewall by running:
sudo chkconfig iptables off
Note: The firewall can be turned on again and configured as per your requirements at a later date.
- Reboot the server by running:
sudo reboot
- After the server has rebooted, log in and verify Selinux is disabled using the command:
sudo getenforce
This returns Disabled.
- Create the directory /opt/zenon by running:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/zenon
- Place the files from your IP to /opt/zenon.
- After unpacking, you will see the directories: sh, trn, trnssl and files: root_cron and zenon_zs.
- Copy the contents of root_cron. Then run:
sudo crontab -e
- Paste the contents of root_cron and save.
- The zenon_zs file is the startup script used by the server to start the TURN services after reboot. Copy this file to the folder /etc/init.d, and make executable.
- Create a link to it in /etc/rc3.d as follows:
cd /etc/rc3.d sudo ln -s /etc/init.d/zenon_zs S99zenonzsstart
Note: This presumes that the runlevel of the server is 3. Typing sudo runlevel at the command line will confirm this. If 5 is returned, create the link in /etc/rc5.d
- To configure the TURN services for UDP on port 14049:
cd /opt/zenon/trn sudo ./configure_trn.sh yourdomain.com X.X.X.X
Where X.X.X.X is the IP of the TURN server interface it will be listening on (typically eth0).
- To configure the TURN service for SSL on port 443:
cd /opt/zenon/trnssl sudo ./configure_trnssl.sh yourdomain.com X.X.X.X
- An MCU password is required for the TURN server to communicate with it, and is stored in these files:
- /opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnuserdb.conf
- /opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnuserdb.conf
- The line starting with mcu: must be noted (or edited in both files if a change is required).
- Finally, reboot the server by typing sudo reboot, and TURN services should be running when the server is brought back up. This can be confirmed using the command sudo ps -elf | grep trn that returns output like this (example output):
root 25313 0.0 0.0 106480 1676 ? S Jul04 107:29 /bin/sh /opt/zenon/sh/trnserver.sh root 25351 0.0 0.0 163860 16052 ? Ssl Jul04 32:32 /opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnserver -v -o -X 72.28.111.195 -a -b /opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnuserdb.conf -f -r mac1.saypage.com root 26443 0.3 0.0 304676 9264 ? Ssl Jul04 579:24 /opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnserver -v -o -X 72.28.111.195 --no-tls -a -b /opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnuserdb.conf -f -r mac1.saypage.com
TURN behind NAT Settings
Note: You only need to perform this step if your TURN server is behind NAT.
- When the TURN server is behind NAT, you must modify the following files:
- /opt/zenon/trn/bin/run.sh
- /opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/run.sh
- Before modification, the first run.sh file will look like this:
/opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnserver -v -o -X <local_ip> --no-tls -a -b /opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnuserdb.conf -f -r <public_realm>
- After NAT modification, the file looks like this:
/opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnserver -o -X <public_ip>/<local_ip> --no-tls -a -b /opt/zenon/trn/bin/turnuserdb.conf -f -r <public_realm>
- Before modification, the second run.sh file for TURN via SSL looks like this:
/opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnserver -v -o -X <local_ip> -a -b /opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnuserdb.conf -f -r <public_realm>
- After NAT modification, the file looks like this:
/opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnserver -v -o -X <public_ip/local_ip> -a -b /opt/zenon/trnssl/bin/turnuserdb.conf -f -r <public_realm>
Notes on TURN Efficiency
For TURN, the networking performance is the most important factor. Make sure that your network has:
- High packet per second (PPS) performance
- Low network jitter
- Low latencies
For example, if you are deploying the TURN server in an AWS instance, then Enhanced Networking is only available on instances launched with HVM AMIs. Preferably, use C3/C4/R3 instances.