Windows NLB Cluster HA Workflows
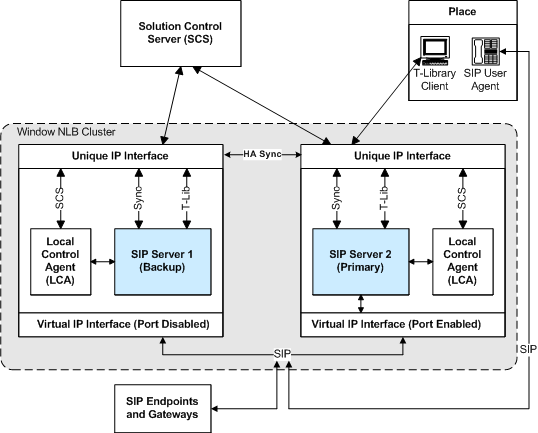
The HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration figure shows a Windows NLB Cluster configuration prior to a switchover.
State Prior to Switchover
State After a SwitchoverTo see what happens in different scenarios, see the following: |
Manual-Switchover Workflow
The following steps describe a switchover workflow for a Windows NLB Cluster configuration (the HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration After a Switchover figure represents the end state of the workflow):
|
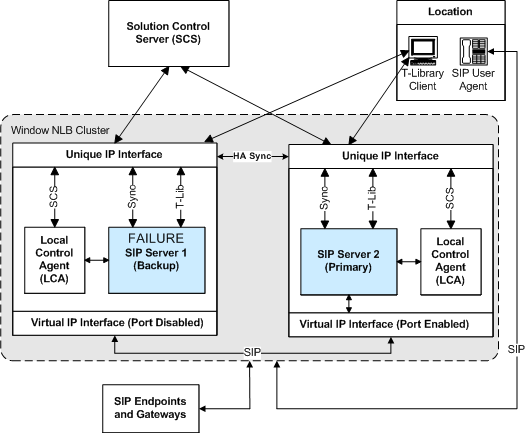
Primary Server-Failure Workflow
The following steps describe a primary server-failure workflow for a Windows NLB Cluster configuration (the HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration After Primary Server Failure figure represents the end state of the workflow):
|
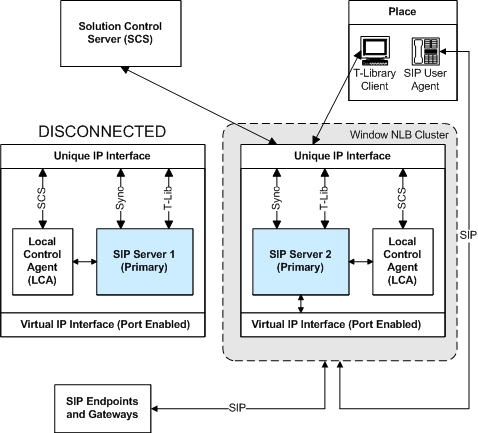
Primary Server-Disconnected Workflow 1
The following steps describe a primary server-disconnected workflow for a Windows NLB Cluster configuration (the HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration After a Primary Server is Disconnected figure represents the end state of the workflow):
|
When the connection to SIP Server 1 has been restored, the following workflow occurs (not depicted in the HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration After a Primary Server is Disconnected figure, above):
- The SCS detects that the connection to SIP Server 1 host has been restored.
- The SCS discovers that both SIP Servers are running in primary mode.
- Through LCA, the SCS instructs SIP Server 1, whose connection was just restored, to go into backup mode.
- SIP Server 1 instructs LCA to launch the Cluster control script on its own host.
- The Cluster control script runs on SIP Server 1, and the Virtual IP port is disabled.
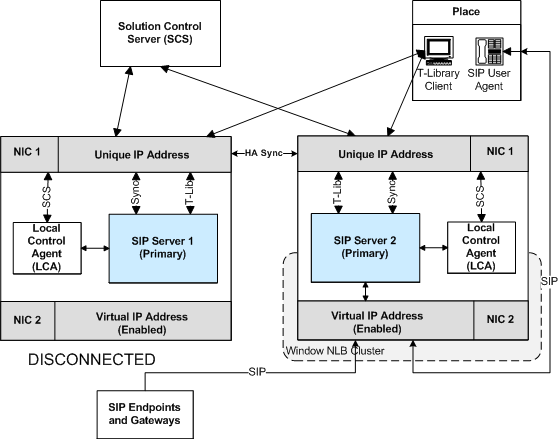
Primary Server-Disconnected Workflow 2
The following steps describe a primary server-disconnected workflow for a Windows NLB Cluster configuration in the scenario where both SIP Servers use two NICs—one NIC is used for SIP communication (NIC 2), while the second NIC (NIC 1) is used for other kinds of communication with other components on the network. The SIP traffic monitoring feature is enabled (the HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration with Two NICs After a Primary Server is Disconnected figure represents the end state of the workflow):
|
When the connection to SIP Server 1 has been restored, the following workflow occurs (not depicted in the HA Windows NLB Cluster Configuration with Two NICs After a Primary Server is Disconnected figure):
- Because the NLB port on SIP Server 1 remained enabled, after network connectivity is restored at NIC 2 on the SIP Server 1 host, the NLB cluster on both hosts is now incorrectly configured"SIP messages are delivered to the NLB cluster node where SIP Server is running in backup mode (SIP Server 1).
- The primary SIP Server (SIP Server 2) detects that it had not received any SIP messages for a certain period of time. SIP Server 2 reports the SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE status to LCA/SCS.
- Through LCA, the SCS instructs the primary SIP Server (SIP Server 2) to go into backup mode and instructs the backup SIP Server (SIP Server 1) to go into primary mode.
- Each SIP Server instructs LCA to launch the Cluster control script on its own host.
- The Cluster control scripts run NLB utilities that disable the Virtual IP port on SIP Server 2 and enable the Virtual IP port on SIP Server 1.